As we approach 2025, it's crucial for both individuals and businesses to have a clear understanding of Medicare tax rates and their implications. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of Medicare tax, its calculation methods, and its significance in funding the U.S. healthcare system.
What is Medicare Tax?
Medicare tax is a federal payroll tax that funds the Medicare program, a government health insurance initiative primarily designed for:
- Individuals aged 65 and older
- Certain younger people with specific disabilities
- People with End-Stage Renal Disease
Key points about Medicare tax include:
- It's part of the Federal Insurance Contributions Act (FICA) taxes
- It's a mandatory contribution for most employees and employers
- The tax funds various aspects of the Medicare program, including hospital insurance (Part A) and medical insurance (Part B)
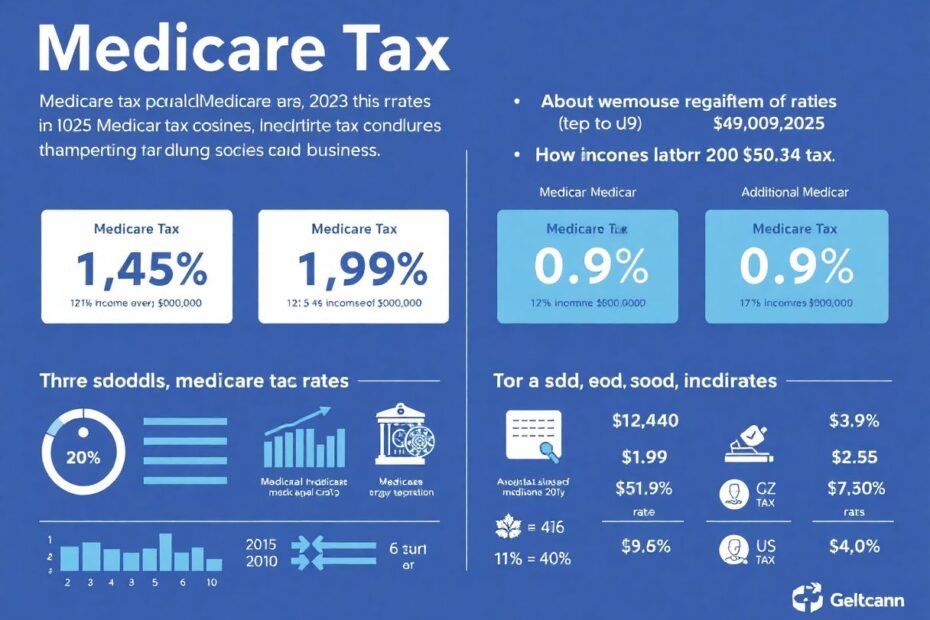
Medicare Tax Rates for 2025
As of 2025, the Medicare tax rate structure remains consistent with previous years:
Standard Medicare Tax Rate:
- Total rate: 2.9% of an employee's eligible wages
- Employee contribution: 1.45%
- Employer contribution: 1.45%
Additional Medicare Tax:
- An extra 0.9% tax on earnings above certain thresholds
- Only paid by high-income earners
- Thresholds:
- $200,000 for single filers
- $250,000 for married couples filing jointly
- $125,000 for married individuals filing separately
Calculating Medicare Tax: Examples and Scenarios
To illustrate how Medicare tax is calculated, let's consider a few examples:
Example 1: Standard Wage Earner
An employee earns $80,000 annually in 2025.
Standard Medicare Tax Calculation:
- Employee contribution: $80,000 x 1.45% = $1,160
- Employer contribution: $80,000 x 1.45% = $1,160
- Total Medicare tax: $2,320
Example 2: High-Income Earner
An employee earns $250,000 annually in 2025.
Standard Medicare Tax Calculation:
- On first $200,000: $200,000 x 1.45% = $2,900 (employee and employer each)
- Additional Medicare Tax: ($250,000 – $200,000) x 0.9% = $450 (employee only)
- Total employee contribution: $2,900 + $450 = $3,350
- Total employer contribution: $2,900
- Total Medicare tax: $6,250
Medicare Tax for Self-Employed Individuals
Self-employed individuals face a unique situation regarding Medicare tax:
- They are responsible for both the employee and employer portions
- The total rate for self-employed individuals is 2.9%
- They may be eligible for a deduction on half of this tax on their income tax return
Example: A self-employed individual with $100,000 in net earnings would pay:
$100,000 x 2.9% = $2,900 in Medicare tax
Impact of Medicare Tax on Businesses
For businesses, especially small and medium-sized enterprises, understanding Medicare tax is crucial for several reasons:
- Budgeting: Employers must account for their portion of Medicare tax in their payroll budgets.
- Compliance: Accurate calculation and timely payment of Medicare tax are legal requirements.
- Employee benefits: Understanding Medicare tax helps in structuring comprehensive employee benefit packages.
Best Practices for Businesses:
- Regularly review payroll processes to ensure accurate Medicare tax withholding
- Stay informed about any changes in tax rates or thresholds
- Consider offering tax-advantaged retirement plans to help employees manage their tax liabilities
Medicare Tax and Healthcare Reform
As we look towards 2025, it's important to consider potential changes in healthcare policy that could affect Medicare tax:
- Proposals for expanding Medicare coverage may impact tax rates
- Ongoing debates about healthcare funding could lead to adjustments in Medicare tax structure
- Technological advancements in healthcare might influence the allocation of Medicare funds
Strategies for Managing Medicare Tax Liability
Both individuals and businesses can employ strategies to manage their Medicare tax liability:
For Individuals:
- Utilize tax-advantaged retirement accounts like 401(k)s and IRAs to reduce taxable income
- Consider the timing of income recognition, especially for high earners
- Explore Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) for tax-advantaged healthcare savings
For Businesses:
- Offer comprehensive benefits packages that include tax-advantaged options
- Implement efficient payroll systems to ensure accurate tax calculations
- Stay informed about tax credits and deductions that may offset Medicare tax costs
The Future of Medicare Tax
Looking ahead to 2025 and beyond, several factors could influence the future of Medicare tax:
- Demographic shifts: An aging population may put pressure on Medicare funding
- Technological advancements: New medical technologies could impact healthcare costs and funding needs
- Policy changes: Potential healthcare reforms may alter the Medicare tax structure
- Economic factors: Overall economic conditions could influence tax policy decisions
Medicare Tax and Social Security
It's important to understand the relationship between Medicare tax and Social Security tax:
- Both are part of FICA taxes
- While Social Security tax has a wage base limit ($160,200 in 2023), Medicare tax does not
- Changes to one system often have implications for the other
International Considerations
For businesses with international operations or employees, Medicare tax presents additional complexities:
- Expatriate employees may have different Medicare tax obligations
- International tax treaties can affect Medicare tax requirements
- Businesses must navigate varying healthcare systems and tax structures globally
Medicare Tax Reporting and Documentation
Proper reporting and documentation of Medicare tax are crucial for both compliance and financial planning:
For Employers:
- Accurate W-2 forms for employees
- Proper quarterly tax filings (Form 941)
- Annual reconciliation through Form 944 or Form 943 for agricultural employers
For Individuals:
- Review of W-2 forms for accuracy
- Proper reporting on individual tax returns, especially for those subject to Additional Medicare Tax
The Role of Technology in Medicare Tax Management
As we move towards 2025, technology plays an increasingly important role in managing Medicare tax:
- Advanced payroll software for accurate calculations and reporting
- AI-driven tax planning tools for individuals and businesses
- Blockchain technology for secure and transparent tax transactions
Medicare Tax and Retirement Planning
Understanding Medicare tax is crucial for effective retirement planning:
- Impact on overall retirement savings strategy
- Consideration of Medicare costs in retirement budgeting
- Interaction between Medicare tax and other retirement-focused taxes
Challenges and Controversies Surrounding Medicare Tax
As with any tax system, Medicare tax has its share of challenges and controversies:
- Debates over the fairness of the tax structure, especially the Additional Medicare Tax
- Concerns about the long-term sustainability of Medicare funding
- Questions about the efficiency of the Medicare system and its impact on tax rates
Educating Employees About Medicare Tax
Employers play a crucial role in helping employees understand Medicare tax:
- Provide clear explanations in employee handbooks and benefit guides
- Offer workshops or seminars on tax and benefit topics
- Ensure HR personnel are well-versed in Medicare tax details to address employee questions
Conclusion
As we navigate the complexities of Medicare tax in 2025, it's clear that this element of the U.S. tax system continues to play a vital role in funding healthcare for millions of Americans. For individuals and businesses alike, staying informed about Medicare tax rates, calculations, and implications is crucial for financial planning and compliance.
By understanding the nuances of Medicare tax, including its standard and additional components, individuals can better manage their tax liabilities and plan for their healthcare needs. Businesses, on the other hand, can ensure compliance, optimize their payroll processes, and provide valuable insights to their employees.
As healthcare policies and economic conditions evolve, it's likely that the Medicare tax system will continue to be a topic of discussion and potential reform. Staying abreast of these changes and understanding their implications will be key to navigating the healthcare and tax landscape in the years to come.
Remember, while this guide provides a comprehensive overview of Medicare tax rates and considerations for 2025, tax laws and regulations can change. Always consult with qualified tax professionals or legal advisors for the most up-to-date and personalized advice regarding your specific situation.